Photo: Mariana Cioato ©
Biodiversity Production Project (JTIBio)
The Biodiversity Production Project (JTIBio) integrates participatory biodiversity monitoring actions and encourages good conservation practices. Its main objective is to contribute to the maintenance and enhancement of ecosystem services on rural properties. The project, an initiative by Japan Tobacco International (JTI) in partnership with SPVS, started in 2014 and has already included 84 small rural landowners in the state of Paraná, directly contributing to the maintenance and enhancement of ecosystem services on rural properties.
Photo: Mariana Cioato ©
Why support the initiative?
Agriculture is intrinsically linked to biodiversity, and its continuity as a business depends on the rational and responsible use of natural resources. Reducing negative impacts on biodiversity means ensuring agricultural productivity, pollination, pest control, soil fertility, water quantity and quality, and hundreds of other ecosystem services.
- The Global Risks Report, released in January 2020 by The World Economic Forum, pointed out for the first time in history that environmental threats are among the top five long-term risks to the economy. The identified risks reinforce the importance of a harmonious balance between wealth generation and the protection of natural heritage, which provides indispensable ecosystem services for agricultural and industrial production and societal well-being.
- SPVS believes that through actions like JTIBio and similar initiatives, designed specifically for each potential partner based on ecological landscape analysis and aligned with effective territory management, biodiversity conservation will gain scale and provide a collective positive impact.
- Good biodiversity conservation practices in rural areas align with this understanding, which, in addition to enabling the maintenance of ecosystem services, allow for agricultural production for current and future generations, ensuring the sector’s sustainability.
- The proposed monitoring and interventions help reduce costs related to water access, pest control, crop pollination, soil fertility, among others.
Photo: Mariana Cioato ©

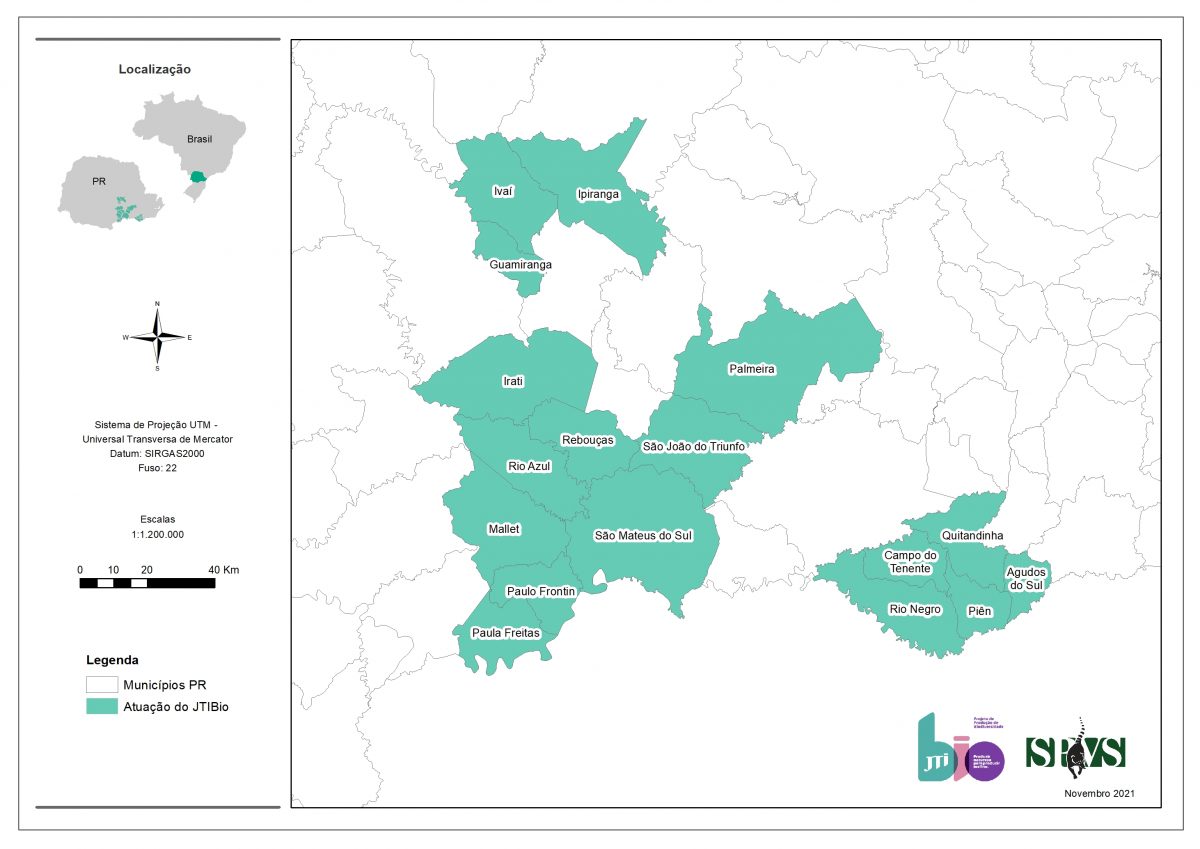
Focus municipalities of the project in Paraná so far:
During the first phase of the Project, technicians from both organizations went to the field to engage with rural producers and understand the environmental reality of properties integrated with the company in Paraná. Based on this data and with support from JTI’s agricultural technicians and producers, it was possible to establish indicators for biodiversity monitoring in the context of small rural properties in the Araucaria Forest and Campos Gerais. For data recording over time, the Participatory Biodiversity Monitoring Protocol was developed, which also guides the landowner on good conservation practices to be implemented on the properties.
Who is it for?
The company Japan Tobacco International (JTI) is the main partner in developing this Project, which serves its chain of rural producers in the state of Paraná. So far, the project has benefited producers in the municipalities of Agudos do Sul, Campo do Tenente, Ipiranga, Ivaí, Mallet, Palmeira, Paula Freitas, Paulo Frontin, Piên, Quitandinha, Rebouças, Rio Azul, Rio Negro, São João do Triunfo, and São Mateus do Sul.
Interested in supporting the Project? Contact us to ask questions and evaluate how to start partnership proposals.
Photo: Mariana Cioato ©
Initiative Results
Existing since 2014, the Project currently includes 84 small rural producers from Paraná, in the municipalities of Agudos do Sul, Campo do Tenente, Ipiranga, Ivaí, Mallet, Palmeira, Paula Freitas, Paulo Frontin, Piên, Quitandinha, Rebouças, Rio Azul, Rio Negro, São João do Triunfo, and São Mateus do Sul. Over the years, the initiative has yielded excellent results, such as:
- Increase in agricultural productivity: where well-preserved natural areas contribute to increased production, especially due to the services offered by pollination and natural pest control.
- Maintenance of ecosystem services: with well-preserved areas, essential services for agriculture, such as water, soil structure and fertility maintenance, and nutrient cycling, have been maintained.
- Capacity development: by being trained, agricultural technicians and producers become more autonomous in agricultural practices shared with conserved nature, ensuring future development and green value in products.
In 2021, 19 technicians from JTI and SPVS met to present dynamics, debates, and exhibitions on topics such as ecosystem services as part of business. In June, July, and August, the phase of technical visits to 43 rural properties participating in the project in 15 municipalities of Paraná was conducted.
Photo: Mariana Cioato ©
Meet those who
Produce the Future with JTIBio


Access
also
Sites and Links
- Radio JTIBio (5th episode): What are Permanent Preservation Areas and how to regularize them?
- Radio JTIBio (4th episode): What are ecosystem services and what do they have to do with agribusiness?
- Radio JTIBio (3rd episode): The importance of ancient forests
- Radio JTIBio (2nd episode): Invasive exotic species
- Radio JTIBio (1st episode): What is JTIBio